Medicare Vs. Medicaid: From Eligibility to Benefits
Picture this: You find yourself at a crossroads, faced with a critical decision that could shape your healthcare journey. On one side stands Medicare, a well-known federal program that caters to the needs of the elderly, individuals with disabilities, and those with end-stage renal disease. On the other side stands Medicaid, a joint federal and state program designed to provide healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families. These two giants, Medicare and Medicaid, are constantly vying for attention, each offering unique eligibility criteria, coverage options, and benefits.
But fear not, for in this blog, we will unravel the complexities of Medicare vs. Medicaid, and take you on a journey from eligibility to benefits. So fasten your seatbelts and get ready to navigate the intricate world of healthcare programs, as we delve into the realm of Medicare and Medicaid to help you make informed decisions about your well-being.
“Medicare is not a handout; it's an earned benefit that we must protect.”- Nancy Pelosi
Defining Medicare and Medicaid
First things first, let's clarify what Medicare and Medicaid actually are. Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily designed for seniors aged 65 and older. It also covers individuals with certain disabilities and those with end-stage renal disease. In a nutshell, Medicare helps provide essential healthcare services to our senior citizens and those who meet specific criteria.
On the other hand, Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that offers health coverage to individuals and families with limited income. Medicaid caters to people of all ages, including children, pregnant women, adults, and individuals with disabilities. It serves as a safety net for those who may not have the financial means to access healthcare services.
7 Key Differences between Medicare and Medicaid
Now that we understand the basic definitions, let's delve into the key differences between Medicare and Medicaid:
| Category | Medicare | Medicaid |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Generally available to individuals aged 65 and older, or younger individuals who have a lasting disability or certain chronic ailments, such as end-stage renal disease (ESRD). |
|
| Federal Funding | Federally funded program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). |
|
| Coverage | Offers standardized coverage through Parts A, B, C, and D.
|
Coverage varies by state. Mandatory services include doctor visits, hospital care, prescription medications, preventive care, and certain additional services determined by each state. |
| Cost-Sharing | Beneficiaries typically pay premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance for Medicare coverage. | Medicaid generally has minimal or no cost-sharing for eligible individuals, but some states may require nominal copayments for certain services. |
| Long-Term Care | Limited coverage for skilled nursing and home health services. | Provides coverage for long-term care services, such as nursing home care, home and community-based services, and assistance for individuals with disabilities. Coverage varies by state. |
| Additional Benefits | Medicare Advantage plans offer additional benefits like dental, vision, and hearing coverage. | Some states offer additional benefits such as dental, vision, and transportation services as part of their Medicaid programs. Benefit offerings vary by state. |
| Enrollment | Individuals can enroll in Medicare during specific enrollment periods, such as Initial Enrollment Period and Annual Enrollment Period. |
|
Medicare vs. Medicaid: Which Program is Right for You?
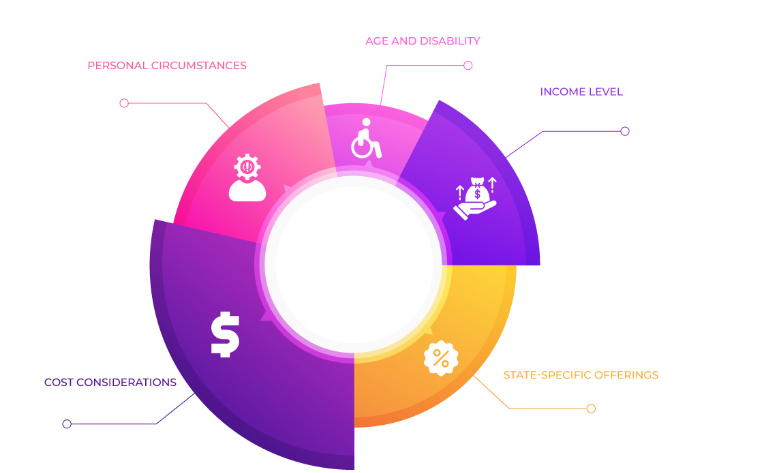
Now that we've explored the eligibility criteria and benefits of Medicare and Medicaid, you may be wondering which program is the right fit for your healthcare needs. Choosing between Medicaid and Medicare requires careful consideration of various factors. So, let's delve into some important considerations to help you make an informed decision:
-
Age and Disability: If you're 65 years or older, Medicare may be the primary option for your healthcare coverage. Medicare provides comprehensive coverage for seniors, including hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription medications. Medicaid, however, extends coverage to individuals of all ages who meet income and other eligibility criteria.
-
Income Level: Medicaid primarily caters to individuals and families with limited income and resources. If you fall within a specific income threshold determined by your state, Medicaid can provide comprehensive coverage. On the other hand, Medicare is not income-based, but beneficiaries may be responsible for premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance based on their specific coverage.
-
State-Specific Offerings: Keep in mind that Medicare as well as Medicaid coverage varies by state. Some states may offer additional benefits like dental care, vision care, and transportation services. If these services are crucial to your healthcare needs, exploring Medicaid options in your state becomes even more important.
-
Cost Considerations: Evaluate the costs associated with each program. Medicare beneficiaries typically pay premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance for their coverage. Medicaid, on the other hand, generally has minimal or no cost-sharing for eligible individuals, ensuring affordability. However, some states may require nominal copayments for certain services.
-
Personal Circumstances: Consider any unique circumstances that may impact your decision. For example, if you require long-term care services, Medicaid may provide more comprehensive coverage in this area. Additionally, if you already have private health insurance coverage, you may need to assess how Medicare or Medicaid would interact with your existing plan.
Ultimately, the decision between Medicare and Medicaid depends on your individual circumstances and healthcare needs. It's advisable to gather all the necessary information, review your options, and consult with healthcare professionals or insurance experts who can provide guidance. At INI, we've assisted countless individuals in obtaining their ideal coverages tailored to their unique needs.
Final Thoughts
So, there you have it—a breakdown of Medicare and Medicaid, from their definitions to the key differences between them. Medicare primarily serves seniors and individuals with specific medical conditions, while Medicaid provides health coverage for low-income individuals and families of all ages. Understanding these programs' eligibility criteria and the benefits they offer is crucial in navigating the complex world of healthcare.
Remember, whether you're eligible for Medicare or Medicaid, it's important to explore the available options, understand your coverage, and make informed decisions about your healthcare needs. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take charge of your well-being!
Did you find this article helpful? Share it!







